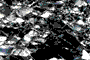
Experimentally deformed feldspar aggregates
Figure caption
45
HA shortened 56% at 1000°C, 10-6/sec, and 1200 MPa; regime 1 dislocation creep.
HA shortened 56% at 1000°C, 10-6/sec, 1200 MPa. This sample has deformed by low temperature dislocation creep (regime 1 of Hirth & Tullis, 1992). Dislocation climb is difficult so original grains work harden due to development of high dislocation densities; recovery occurs by bulging recrystallization (the driving force is high even though the grain boundary mobility is low). Original grains in this sample have become separated into several lozenge-shaped grains along deformation bands or grain-scale faults; these new boundaries as well as original grain boundaries have developed a zone of extremely fine (d~1 µm) recrystallized grains, which are initially strain-free and thus much weaker than the work-hardened original grains. They maintain this weakness because they are easily and continually swept by new episodes of grain boundary migration as soon as they develop a high dislocation density. (W395)