CET/UWA Microstructure Course
CET/UWA Microstructure Course CET/UWA Microstructure Course
CET/UWA Microstructure Coursegrain considerably larger than the matrix which is a relict of an earlier grain size
Grain formed during metamorphic growth which is considerably larger than the matrix
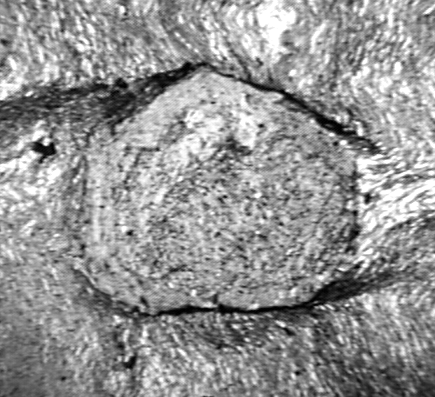
porphyroblast which has grain boundaries controlled by its own crystallography
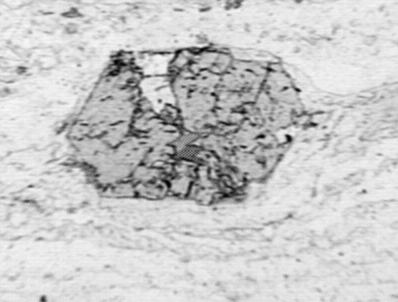
porphyroblast which does not have grain boundaries controlled by its own crystallography. The two porphyroblasts below are idioblastic with respect to the matrix, but xenoblastic with respect to each other inclusion trail relic matrix grains included and then shielded by growing porhyroblast, often preserving pre-exiting foliation

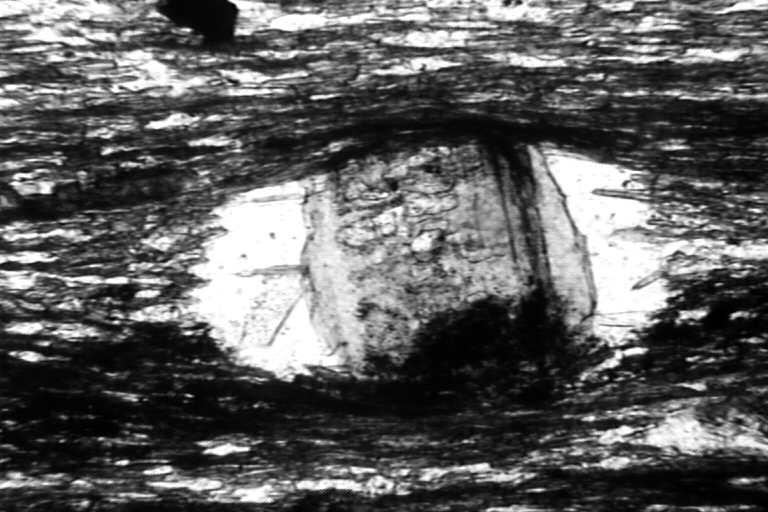
porphyroblast extremely rich in inclusions. The top 85% of the picture below is one grain, filled with inclusions of other minerals

inclusion trail preserving pre-existing crenulated foliation. The inclusion trail in the inclusion trail porphyroblast picture is probably helicitic.
garnet or other mineral formed in shear zone where rotation of porphyroblast during growth has resulted in spiral inclusion trail
areas of matrix adjacent to porphyroblast or porphyroclast in which matrix pulls away from hard mineral and a dilatent site forms which is filled with the fibrous growth of a new mineral, often quartz
areas of matrix adjacent to porphyroblast or porphyroclat which are shielded by strong mineral and show equant (undeformed?) grain shapes of a mineral, often quartz. Pressure shadows could also represent recrystallised pressure fringes.
rock which has undergone significant grain size reduction (usually as a result of a dynamic recrystallisation process). Shear zones are often made up of mylonites.
S= schistocité = cleavage plane C= cisaillement = shear plane A shear zone microstructure where two foliations are present, a C plane parallel to the shear zone boundaries, often marked by mica orientations, and a cleavage plane defined by the grain shape foliation of other minerals such as quartz, which makes an angle with the C planes that decreases with increasing strain.
lozenge shaped mica porphyroblasts forming an oblique foliation at an angle to the shear zone boundaries, with thin mica layers running off each end of the lozenge.
microstructure distinguished by distinct domains of different character, such as different grain shape foliation orientation, or as below, different CPO. The diagonal bands in this thin section each consist of grains in with similar orientations within each band, but different orientations between bands.