Lab 5A-Vein & stylolite movies
 CET/UWA Microstructure Course
CET/UWA Microstructure Course
| TOC
| Lecture 1
2
3
4 a
b
5 a
b
| Lab 1 a
b
c
2 a
b
c
3 a
b
4 a
b
5 a
b
| Glossary Table
1
2
3
4
5
Index
| GEOS5505 Lab 1
|
1) Different vein types
Lecture 5.b deals with the various types of veins and their internal
structures. It also contains a few movies that show the development of
the vein types over time.
-
Look up and read through lecture 5.b and watch the
movies until you think you understand the differences between the various
types well enough.
-
Which vein types can give you the correct opening
trajectory (provided the crystals are tracking 100%)?
-
Why is it important to know of which type a vein
is (say antitaxial or syntaxial) if you want to know the opening trajectory?
Look up movies
in lecture 5.b
2) Stylolite movie
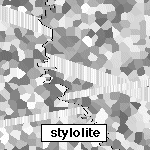
This is the movie of a developing stylolite that you can also find in
lecture 5.b. Play the
movie and answer the following questions:
-
What is the relation between the direction in which
the stylolite "teeth" point and the shortening direction?
-
Two older veins are off-set by the stylolite. Explain
the difference between these off-sets and those caused by a (small) shear
zone. How would you distinguish between the two?
(3) Computer simulation of crack-seal growth
Four movies were made with a 2-dimensional computer model that simulates
the growth of a vein by the crack-seal mechanism. The movies show how several
factors play a role in determining the shape and orientation of crystals
in a vein:
-
crystallographic orientation
-
growth anisotropy of crystals
-
magnitude and direction of opening increment per crack-event
-
shape of crack
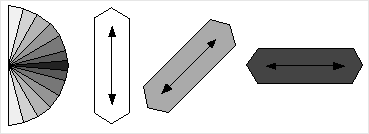 The movies
show repeated cracking and sealing on one side of a vein crystals subsequently
filling (sealing) the crack from one side only. This is thus an asymmetric
vein, but can also be regarded as one side of an antitaxial vein. The 'mineral'
that fills the vein is somewhat like quartz. It has one fast growth direction
(// to C-axis) and would, if allowed to grow in free space, grow into a
shape as shown in the picture. Each crystal is shaded grey according to
the orientation of its C-axis. Horizontal C-axes are dark and vertical
ones are white.
The movies
show repeated cracking and sealing on one side of a vein crystals subsequently
filling (sealing) the crack from one side only. This is thus an asymmetric
vein, but can also be regarded as one side of an antitaxial vein. The 'mineral'
that fills the vein is somewhat like quartz. It has one fast growth direction
(// to C-axis) and would, if allowed to grow in free space, grow into a
shape as shown in the picture. Each crystal is shaded grey according to
the orientation of its C-axis. Horizontal C-axes are dark and vertical
ones are white.
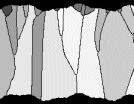

Movies A&B

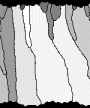
Movies C&D
Watch the four movies and then answer the following
questions
-
Describe the internal structures in the 4 veins (grain
shape, orientation, etc.)
-
Does a crystallographic preferred orientation develop,
and if so, which? (are there certain "winners" and "losers"?)
-
What is the opening trajectory in each case and how
much of it is reflected in the shape of the grains?
-
Can you relate your observations to the 4 factors
listed above that may determine the internal structure in the veins?
Continue with part (B) of this lab.
 CET/UWA Microstructure Course
CET/UWA Microstructure Course CET/UWA Microstructure Course
CET/UWA Microstructure Course



